
Doppler correctly predicted that the phenomenon should apply to all waves, and in particular suggested that the varying colors of stars could be attributed to their motion with respect to the Earth. The hypothesis was tested and confirmed for sound waves by the Dutch scientist Christoph Hendrik Diederik Buys Ballot in 1845. The effect is named after Christian Andreas Doppler who offered the first known physical explanation for the phenomenon in 1842. The history of the subject begins with the development in the nineteenth century of wave mechanics and the exploration of phenomena associated with the Doppler effect. Hippolyte Fizeau who first described the Doppler redshift
Yet a third type of redshift, the gravitational redshift also known as the Einstein effect, results from the time dilation that occurs in general relativity near massive objects. This relation is accounted for by models that predict the universe is expanding, seen in, for example, the Big Bang model. This Doppler redshift phenomenon was first predicted and observed in the nineteenth century as scientists began to consider the dynamical implications of the wave-nature of light.Īnother redshift mechanism accounts for the famous observation that the spectral redshifts of distant galaxies, quasars, and intergalactic gas clouds are observed to increase proportionally with their distance to the observer.
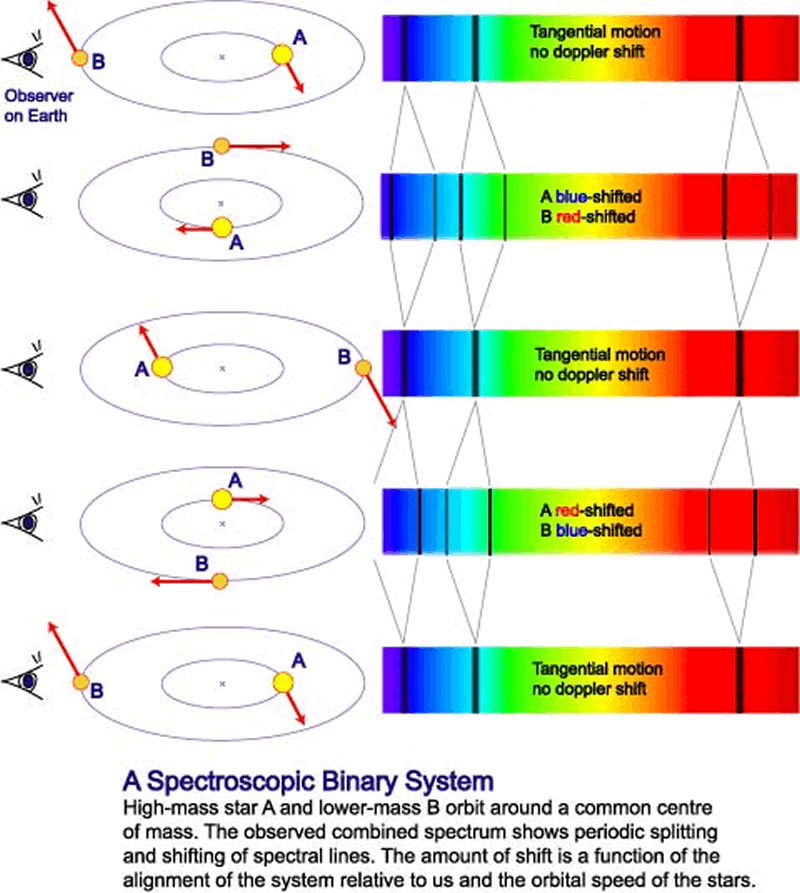
Doppler radar and radar guns), spectroscopic astrophysics uses Doppler redshifts to determine the movement of distant astronomical objects. Although observing such redshifts has several terrestrial applications (e.g. infrared, microwaves, and radio waves), redshifts shift the radiation away from the red wavelengths.Ī redshift can occur when a light source moves away from an observer, corresponding to the Doppler shift that changes the frequency of sound waves. This nomenclature might be confusing since, at wavelengths longer than red (e.g. Conversely, a decrease in wavelength is called blueshift.Īny increase in wavelength is called "redshift" even if it occurs in electromagnetic radiation of non-optical wavelengths, such as gamma rays, x-rays and ultraviolet. This increase in wavelength corresponds to a decrease in the frequency of the electromagnetic radiation. More generally, redshift is defined as an increase in the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation received by a detector compared with the wavelength emitted by the source. In physics and astronomy, redshift occurs when the visible light from an object is shifted towards the red end of the spectrum.

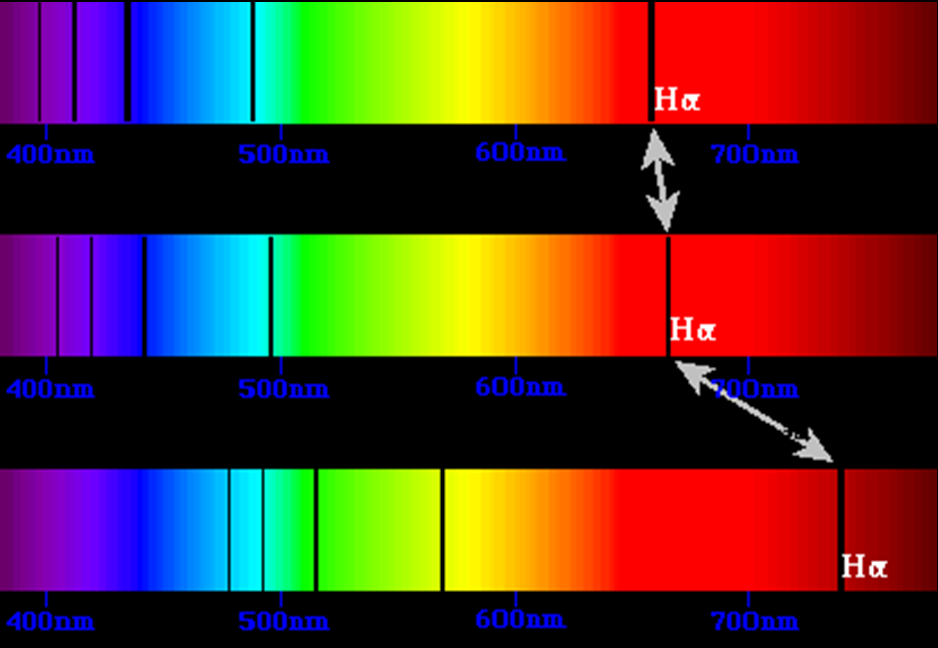
Wavelength increases up towards the red and beyond, (frequency decreases) Redshift of spectral lines in the optical spectrum of a supercluster of distant galaxies (right), as compared with that of the Sun (left).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
